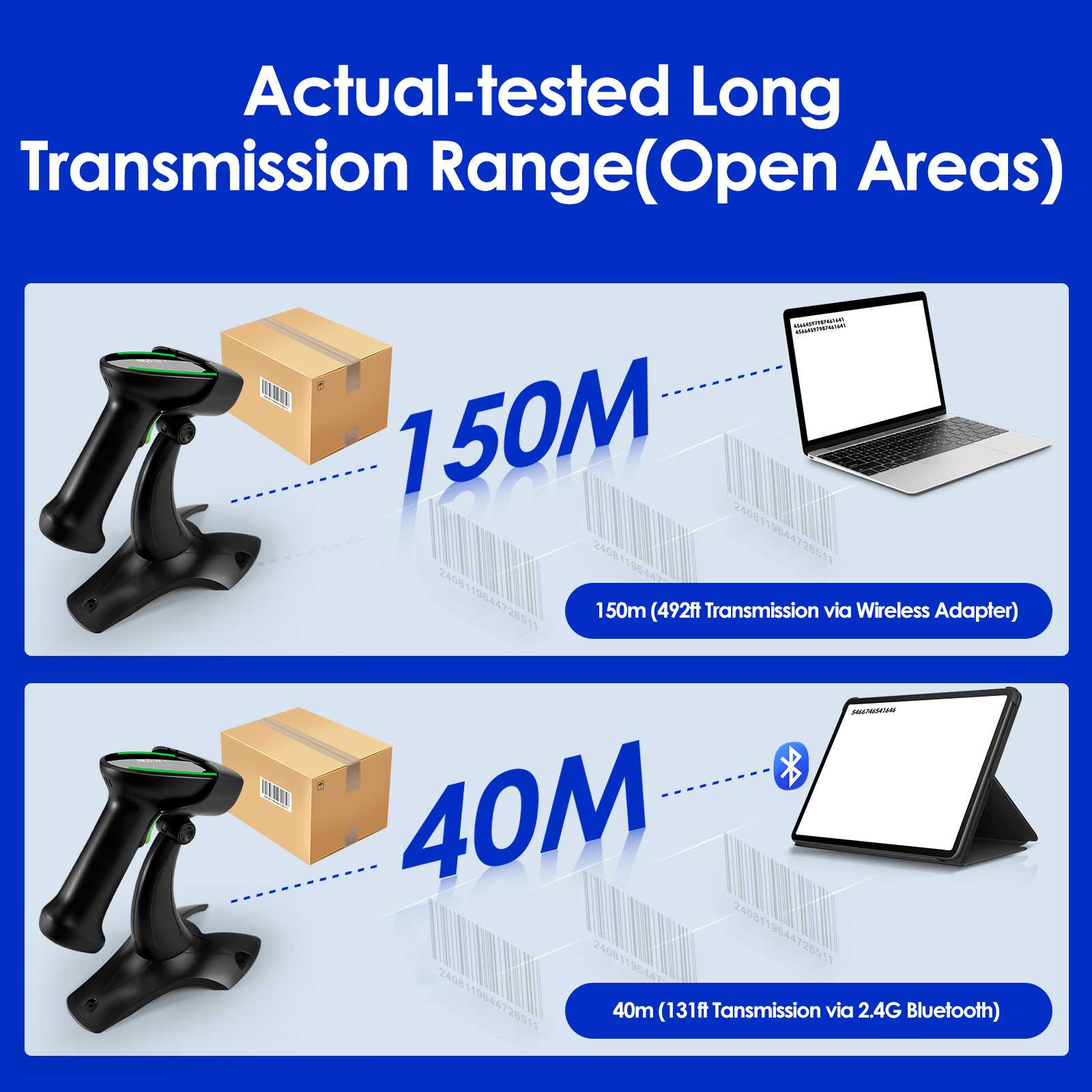
What is barcode
A barcode is a machine-readable language composed of black and white bars arranged in specific patterns. These patterns encode data such as product numbers, serial codes, or inventory details, enabling rapid and accurate information capture. Since their invention, barcodes have revolutionized industries by streamlining processes like retail checkout, asset tracking, and supply chain management. Today, over 225 types of one-dimensional (1D) barcodes exist, including widely adopted standards like UPC, EAN, Code 39, and Code 128.

The Anatomy of a Barcode
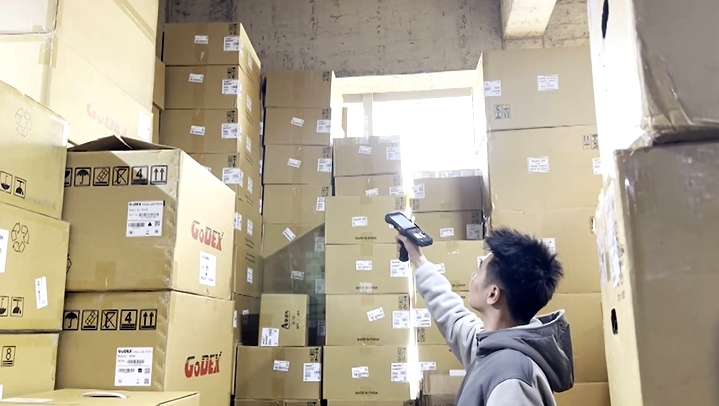
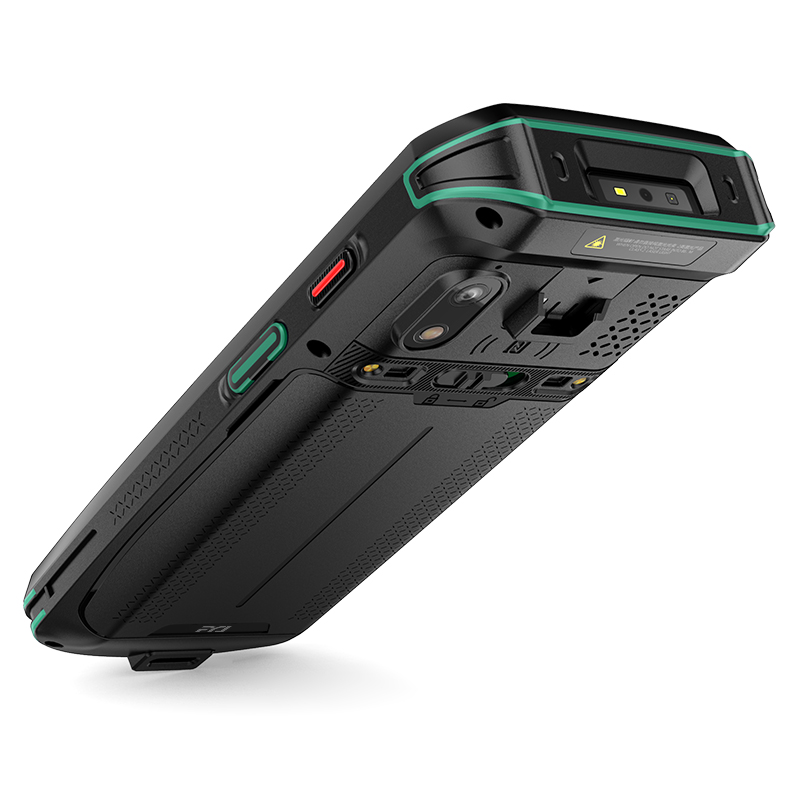
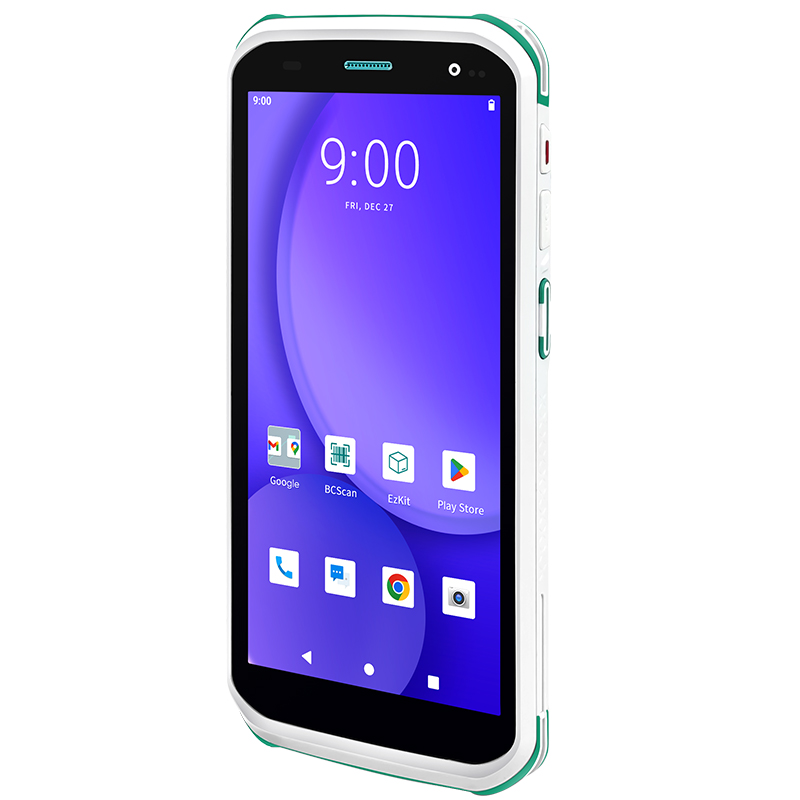
Every barcode contains three core components: a quiet zone (blank margins to signal scanning readiness), start/stop characters (indicating code boundaries), and data characters (the encoded information). The width ratio of bars and spaces, known as the "X dimension," ensures compatibility across scanners and printers. Advanced handheld barcode scanners, such as those integrated into modern industrial PDA devices, leverage these structural elements to decode data efficiently, even in challenging environments like warehouses or outdoor settings.

1D vs. 2D Barcodes: A Quick Comparison
Traditional 1D barcodes store data horizontally, ideal for simple identifiers like product SKUs. In contrast, 2D barcodes (e.g., QR codes) encode data both horizontally and vertically, offering higher capacity for complex information like URLs or batch details. While 1D codes remain prevalent in retail, industries adopting mobile inventory management tools increasingly rely on 2D codes for real-time data access and error-free logistics.


Why Barcode Scanning Technology Matters
Efficient barcode scanning minimizes human error and accelerates workflows. For businesses, integrating industrial PDA devices with high-precision scanners ensures seamless operations—from inventory audits to shipment verification. These rugged, portable tools are designed to withstand drops, dust, and extreme temperatures, making them indispensable in sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.

Empowering Modern Workflows
Whether tracking assets in a warehouse or processing transactions in retail, barcodes bridge the gap between physical items and digital systems. By deploying handheld barcode scanners paired with intuitive software, companies unlock real-time visibility into their operations. For instance, mobile inventory management tools enable instant updates to centralized databases, reducing stockouts and optimizing supply chains.
Barcodes are more than black-and-white lines; they are the backbone of modern automation. Investing in robust scanning solutions like industrial PDA devices or mobile inventory management tools ensures businesses stay agile in a data-driven world. As technology evolves, these tools will continue to redefine efficiency, accuracy, and scalability across industries.

-end-